To understand rotation about a fixed axis. Consider the motion of a couple of points within the rigid body the blue point at a large radius travels further in the same time than the red point so although the angular speed is the same.
Kinetic energy of a solid.

. To understand center of mass and moment of inertia. The kinetic energy is T i. The wheel or rotor of a motor which appears in rotation motion problems is a common example of the rotational motion of a rigid body.
The geometry is illustrated in figure 23. Nicolaus Copernicus 1473-1543 Rotation vector of a moving rigid body andor frame of reference. Rigid body rotation is featured prominently in science sports and engineering.
A rigid body is an object with a mass that holds a rigid shape. Physics 111N 2 rotations of a rigid body. Rotational inertia for a rigid body is I m ir i2 and is measured in SI units of kilogrammeters2.
But the linear velocity is also dependent on the distance of particles from axis of rotation. Since the bod y is rigid Ri is a fixed distance for each i and ωis the same for all particles in the body. The problems involving pure rotation can be analyzed using the kinematic equations for rotational motion and applying the equation τ I α where τ is the net torque about the axis of rotation I moment of inertia of the rigid body about the axis of rotation and α angular acceleration of the rigid body about the axis of rotation.
In other words the rolling motion of a rigid body can be described as a translation of the center of mass with kinetic energy Kcm. Sum of its translational and rotational energies. In the present work we investigate the perturbed rotational motions of a symmetric rigid body gyrostat about a.
Movement of a coin over a carrom board Properties of Rigid Body Motion. This point can be on the body or at any point away from it. Every motion of a rigid body about a fixed point is a rotation about an axis through the fixed point.
Because the motion of the body in question is from the reference configuration to the current configuration this axis depends on the choice of reference configuration. The axis referred to here is the rotation axis of the tensor. This diver is moving.
In rotational motion of the rigid body all the particles cover the same angular displacement in a particular interval. Rotation requires the idea of an extended object. Angular momentum equals moment of inertia times angular velocity.
The moments of inertia for different regular shapes are shown in Figure 2. A stone falls straight at the surface of the earth. The particles lying on the axis of rotation remains stationary.
To understand rolling motion. Motion of points in a rigid body. In rotational motion only rigid bodies are considered.
To understand the equilibrium of an extended object. This motion can be rectilinear or curvilinear. The axis of rotation may lie inside the body or even outside the body.
Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis The figure below shows a rotating body that has a point with zero velocity about which the object undergoes rotational motion. An axis of rotation of a body is a line in space about which the particles within the body maintain a constant distance and therefore move in a circular path about the axis. A rigid body can have two types of motions when forces are applied to it.
Since the body undergoes rotation OA OA OB OB. The proper motion of a sphere is rotation in a circle. Consider a rigid body undergoing rotation about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the paper and passing through O.
Rotational Motion of a Rigid Body - Towson University. A pure rotational motion is when a body spins around a fixed internal axis. Figure 2 Moments of inertia for various regular shapes.
Suppose that A and B are any two particles of the rigid body at the position 1 while A and B are their subsequent locations when the body is at the position 2. To understand the circumstances under which objects sitting on a surface are stable or unstable. Moving by Bus Sailing of Boat Dog walking A person shaking the plant.
The body and let Ri be the perpendicular distance of the ith particle from the rotation axis. To extend the particle model to the rigid-body model. Rotation of a Rigid Body Not all motion can be described as that of a particle.
The fact that the particle is rotating does not change its energy of motion because the kinetic energy of the particle depends only on its mass and speed. These kinds of bodies are usually a continuous distribution of mass. Mechanics problems frequently include both.
In an ideal scenario these bodies do not change their shape or deform. Six independent coordinates are required to completely specify the position and orientation of a rigid body. So the angular velocities of all the particles will be the same.
Many objects of interest however are very well approximated by the assumption that the distances between the atoms in the body are fixed. Describing the motion of such a system without some simplifications is clearly impossible. Theoretically it is a collection of particles that are at a fixed distance from one another.
Rotational Motion Configuration Space for a Rigid Body. Image will be Updated soon Common examples of Rotational Motion are. Rigid Body Motion and Rotational Dynamics 131 Rigid Bodies A rigid bodyconsists of a group of particles whose separations are all fixed in magnitude.
A rigid body is said to have pure rotational motion if every particle of the body moves in a circle the centre of which lies on a straight line called the axis of rotation Fig. Translational Motion A body is said to be in translatory motion when all the particles on that body are moving the same distance in equal time intervals. For example the location of the first particle is specified by three coordinates.
The motion of motors gears wheels top ferris wheel etc. A macroscopic body is made up of a very large number of atoms. Abstract and Figures.
In a rotational motion all the constituent particles of the rigid body undergo circular motion about the common axis.

Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7 Learn Cbse Physics Notes Physics Motion

Physics Mechanics 3 Rotational Motion Moment Of Inertia Angular Momentum Torque Youtube Physics Physics Mechanics Science

System Of Particles And Rotational Motion 2016 Vol 12 Mtg Physics For You Physics Formulas Physics Notes Physics Concepts

Physics Mechanics 3 Rotational Motion Moment Of Inertia Angular Momentum Torque Youtube Physics Physics Mechanics Math

Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7 In 2022 Physics Body Systems Particles

Revision Notes On Circular And Rotational Motion Askiitians Physics Notes Revision Notes Motion Physics

Physics Mechanics 3 Rotational Motion Moment Of Inertia Angular Momentum Torque Youtube Physics Physics Mechanics Science For Kids

Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7 Learn Cbse Basic Physics Formulas Physics Concepts Physics Notes

Physics Mechanics Motion Of Rigid Body Physics Formulas Science Physics Mind Maps Advanced Level Ph Physics Concepts Physics Formulas Learn Physics

Gravitation Cbse Notes For Class 11 Physics Learn Cbse Class11physicsnotes Gravitationphysicsclass11 Physics Notes Physics Physics Lessons

Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7 Learn Cbse Physics Notes Physics Particles

Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7 Learn Cbse Basic Physics Formulas Physics Concepts Physics Notes

Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7 Physics Notes Physics Class

Rotational Motion Examples Motion Physics Interactive Physics Motion

Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7 Learn Cbse In 2021 Physics Physics Notes Motion Physics
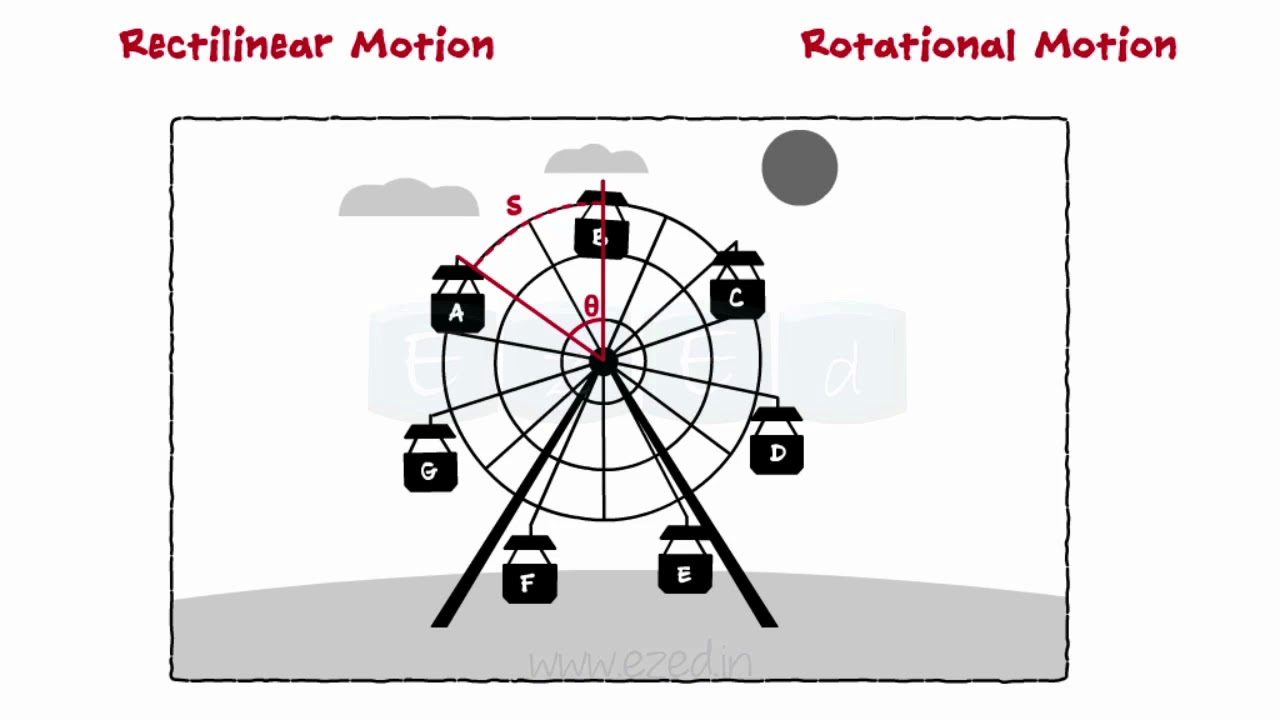
Kinematics Of Rigid Bodies Translation And Rotation About Fixed Axis Body Rotating Mechanical Engineering

Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7 Learn Cbse Physics Physics Notes Particles

Newton S Second Law Solved Problem D Alembert S Principle Newtons Second Law Solving Equations Problem Solving

Rotation About A Fixed Axis Body Diagram Equations Rotating

